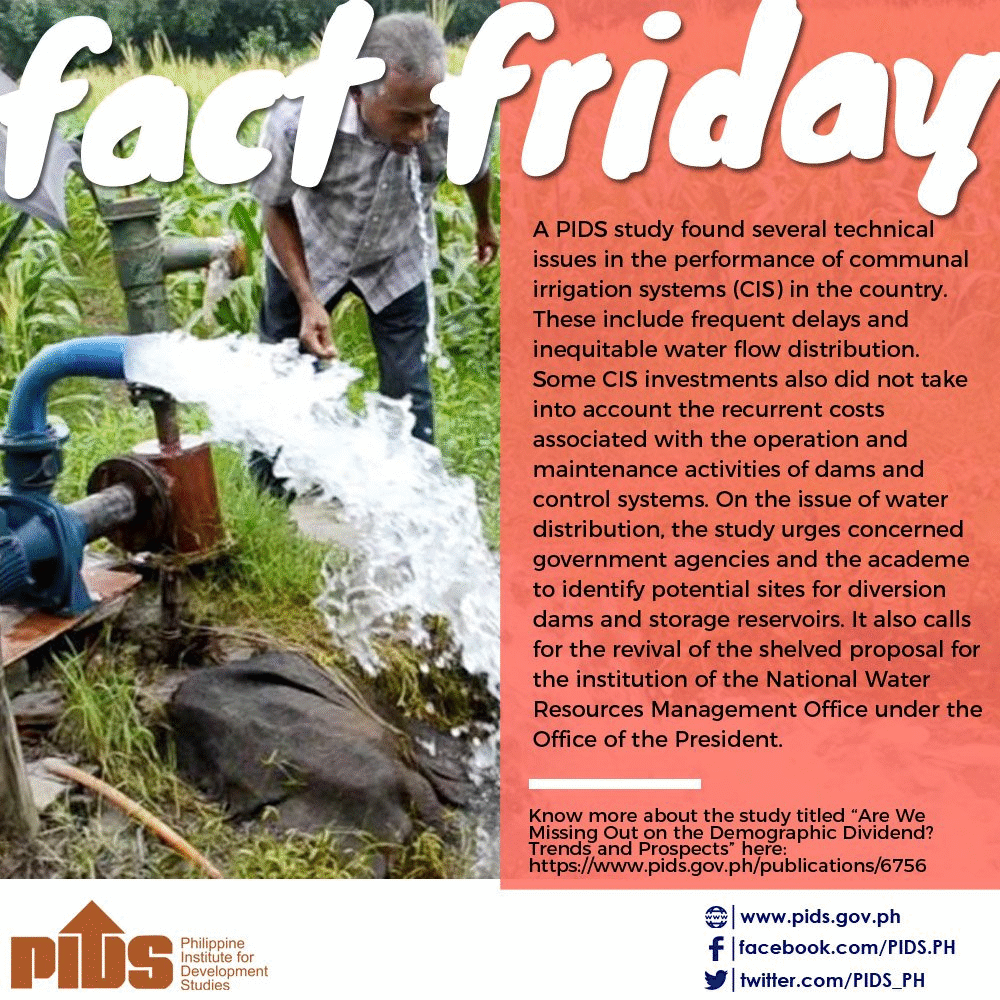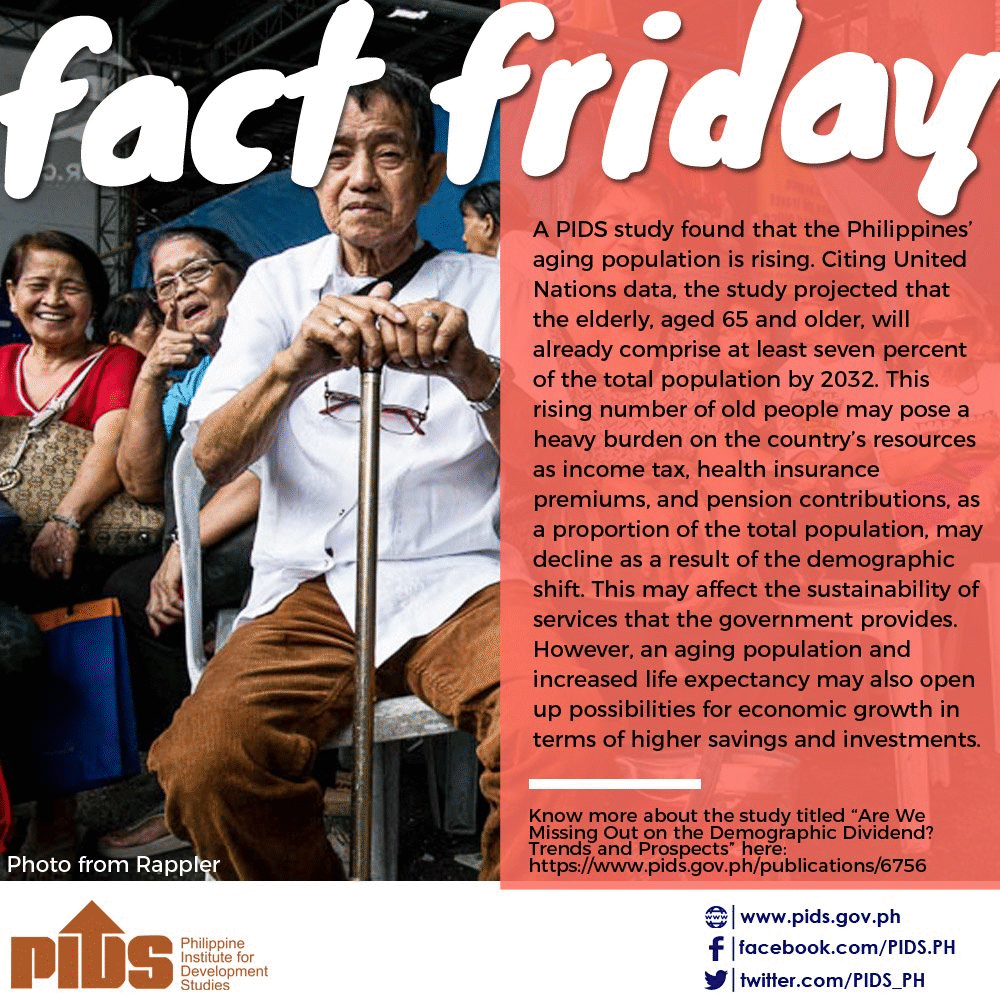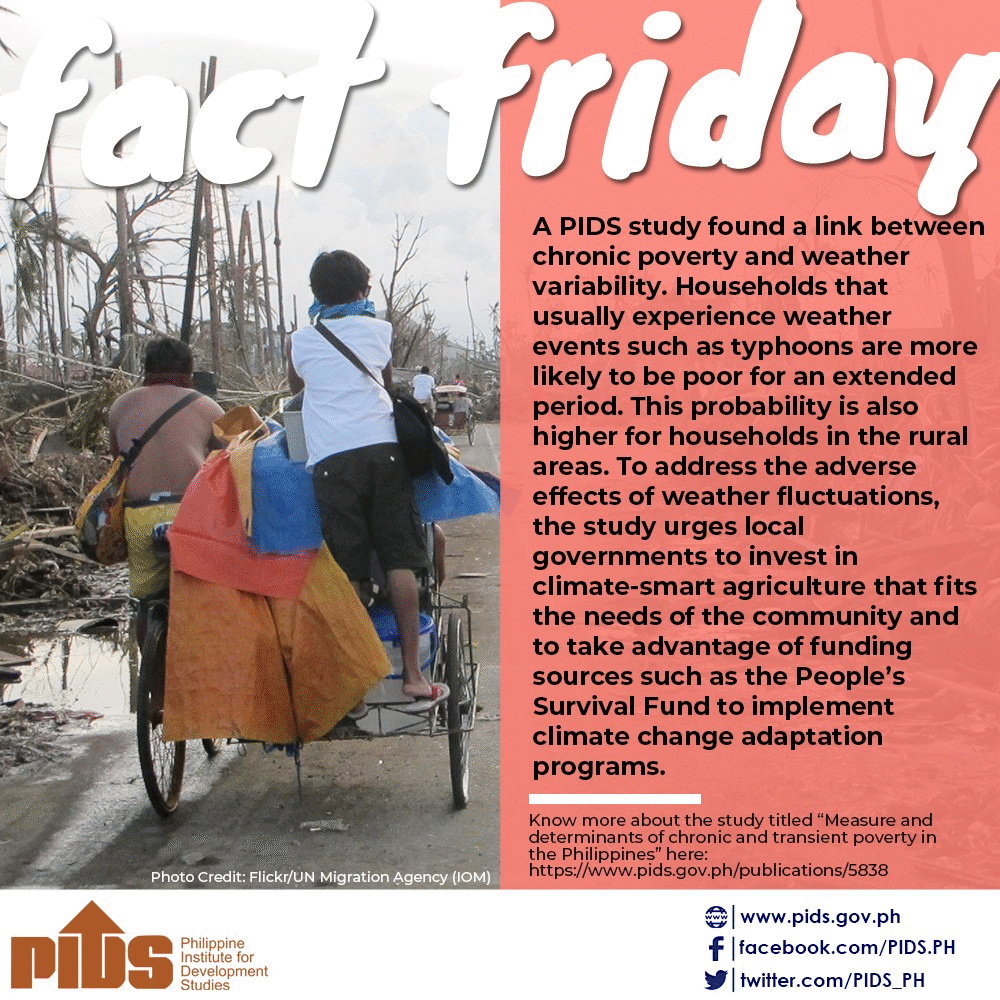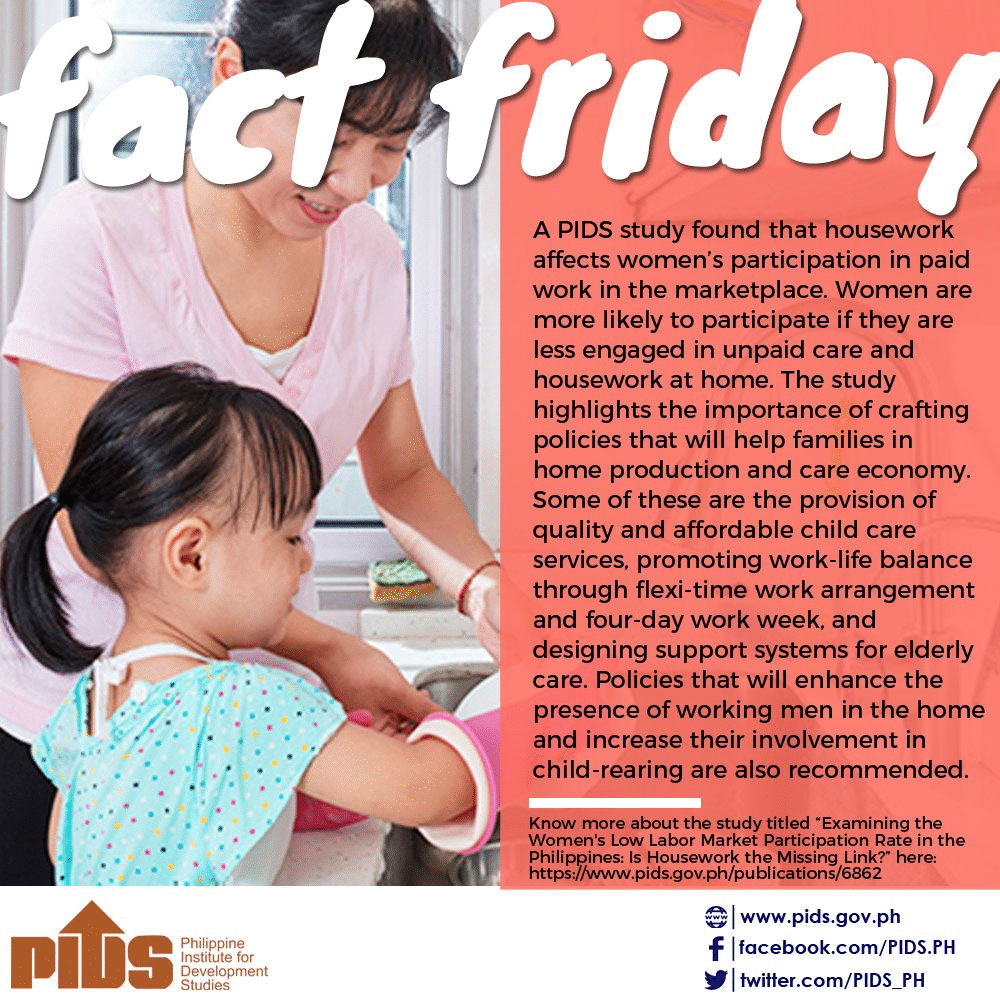Having trouble reading this email? View it in your browser. |
||||
 |
||||
|
||||
In 2018, the Philippine Institute for Development Studies (PIDS) continued to pursue its research agenda of resilience capacity building. This Annual Report highlights, among others, the Institute's accomplishments in terms of completed research studies and knowledge-sharing and advocacy activities conducted to bring the results of its policy studies closer to its target audiences and continuously inform the policymaking process. It also revisits the year’s Development Policy Research Month celebration, which carried the theme “Harnessing the Fourth Industrial Revolution: Creating Our Future Today”.
PIDS Book 2009-01:
Harnessing the Fourth Industrial Revolution: Creating Our Future Today (Proceedings of the Fourth Annual Public Policy Conference 2018) The advent of the Fourth Industrial Revolution (FIRe) has dramatically changed the world we live in. The FIRe, characterized by the fusion of the physical, digital, and biological worlds, is radically transforming businesses and poses risks that may highly impact our society. To better understand its potential socioeconomic impacts and benefits for the country, the Philippine Institute for Development Studies dedicated the Fourth Annual Public Policy Conference (APPC) held in September 2018 to the discussion of this topic through the theme "Harnessing the Fourth Industrial Revolution: Creating Our Future Today".
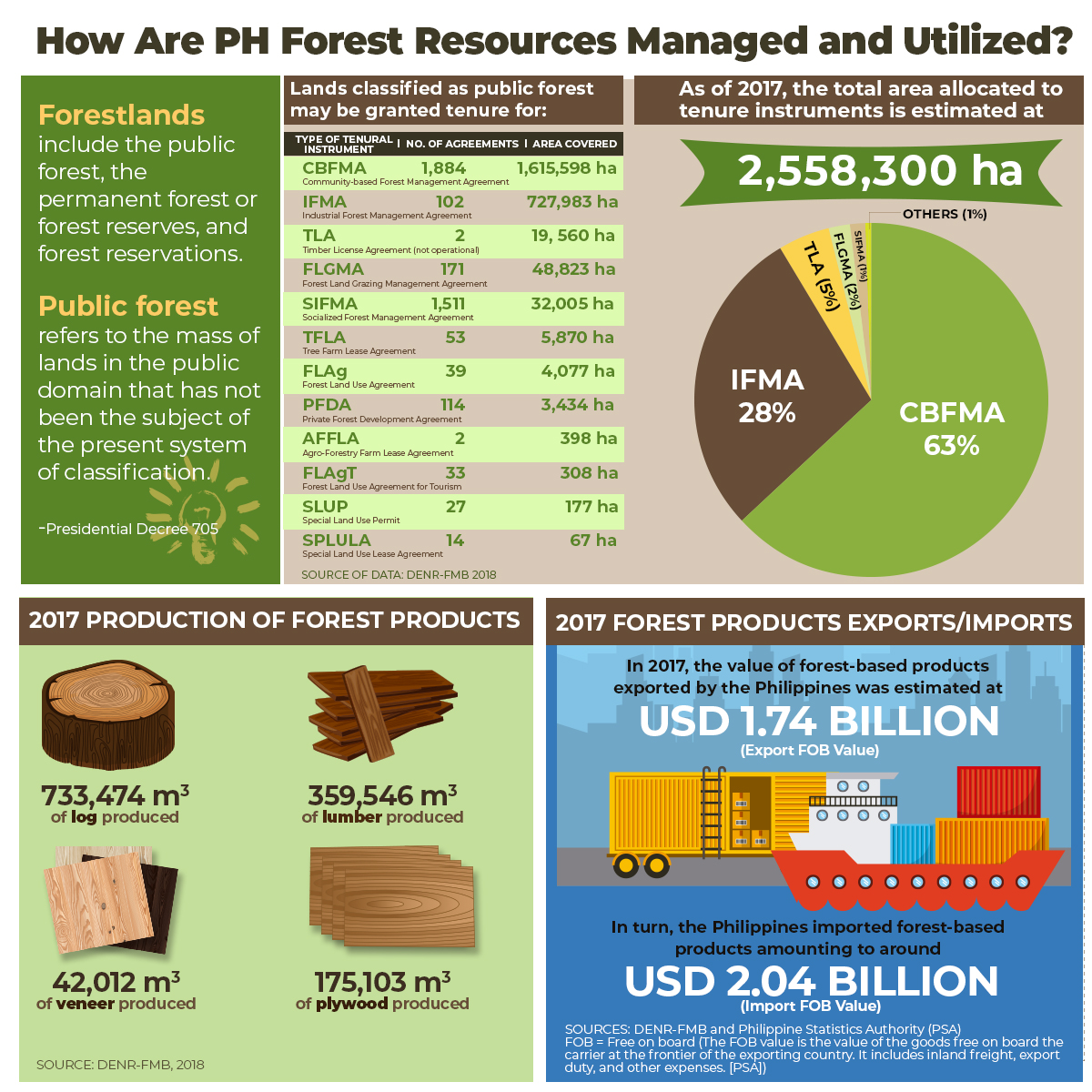
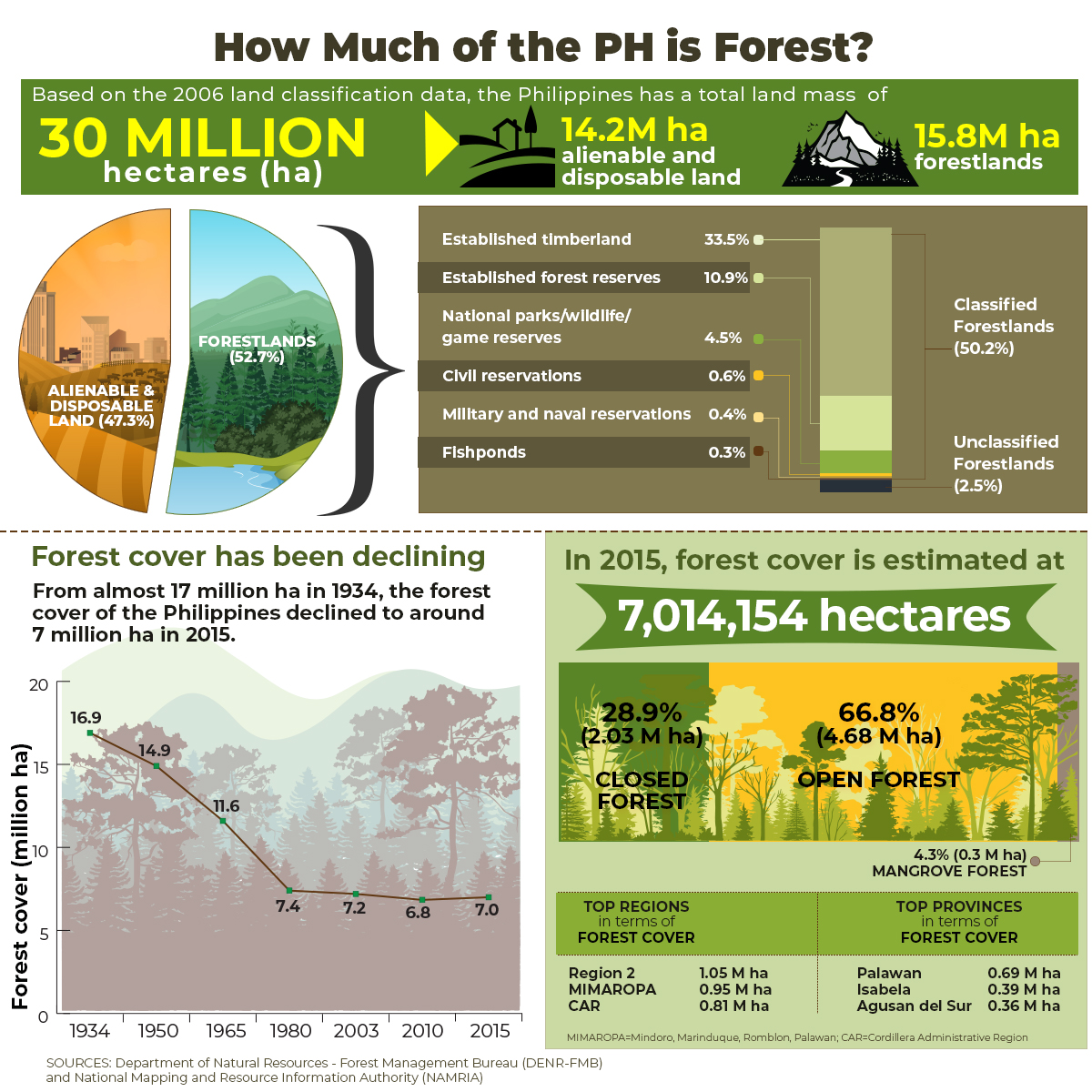
RPS 2019-03: Forest Protection in the Philippines: Policy Evolution and Sector Outcomes This paper looks into three forest protection initiatives across three case study areas, namely, tenurial arrangements, apprehension and enforcement mechanisms, and the National Greening Program (NGP). Lapses in the implementation process characterized by the absence of site-species matching and failure to incorporate site demographics and topographical issues, and weak institutionalization of the legal support, particularly at the subnational level, remained present. In response, best practices were identified from each area and recommendations were drawn to improve the current policy landscape. These included the use of controlled use zones as management tool, stronger interface with local stakeholders, strengthening of legal support for City Environment and Natural Resources Office, use of Electronic Filing and Monitoring System portal, institutionalization of the Lawin Program, practice of site-species matching, and stronger stakeholder participation in the NGP. Reforms in the structure of oversight agencies and an update in the national baseline policy were sought in the form of an Environmental Protection and Enforcement Bureau proposal and the persistent lobbying for the Sustainable Forest Management Bill. Click here to download the paper.
POLICY NOTES PN 2019-08: Evaluation of National Irrigation Systems in the Philippines National irrigation systems (NIS) are crucial to the Philippine agriculture sector. Currently, they account to about half of the area that supply rice in the country, making their operation and maintenance critical in the food sufficiency program of the government. Despite the huge budget allocated to the National Irrigation Administration (NIA), however, many NIS are underperforming based on selected indicators. For instance, this study finds that NIS are still suffering from various issues, such as siltation, flooding, deterioration of canals, and other institutional and policy issues. Some of the NIS also experience salinity problems, which can pose serious effects on crop production and yield. To address these issues, the study urges the government to adopt good watershed management and enhance maintenance and rehabilitation of NIS facilities, including pipe network. It also calls for the regular monitoring and proper implementation of policies related to illegal activities that affect irrigation system functionality, such as those relating to illegal settlers, pumping, and waste disposal. Click here to download the paper. PN 2019-07: Issues on Communal Irrigation Systems in the Philippines Despite massive efforts and funding to support irrigation development, the increase in irrigated areas has been minimal in the Philippines, particularly in Mindanao. To expand the irrigation base, new irrigable areas may be served by small-scale systems, such as the communal irrigation systems (CIS). This Policy Note presents an assessment of select CIS in the Philippines. Among others, it finds that several technical problems confront the performance of CIS. These include the frequent delays and inequitable water flow distribution, as well as CIS investments that do not also take into account the recurrent costs associated with operation and maintenance activities of dams and control systems. On the issue of water distribution, the study recommends the concerted effort on the part of concerned government agencies and even the academe to identify potential sites for diversion dams and storage reservoirs. It also calls for the revival of the shelved proposal for the institution of the National Water Resources Management Office under the Office of the President. In terms of the issues concerning investments, the study urges the government to focus on the improvement of planning and budgeting of the operation and maintenance activities of CIS. Click here to download the paper. PN 2019-06: Mobilizing Local Governments To Prevent Child Stunting This Policy Note reviews the current international and national focus on child stunting prevention, including health and nutrition programs and status of nutrition outcomes among mothers and children. It finds that while the national government has already devolved the implementation of health and nutrition programs, these interventions have yet to produce sufficient national impact. It notes a number of factors that limit the performance of local governments in the prevention of child stunting. These include the difficulty of aligning their priorities with national targets, aggravated by inadequate local data for priority setting, and the limited local resources for health and nutrition. To address these issues, the study urges the national government to develop a comprehensive national guideline and operational strategies to guide local governments and likewise suggests adoption of local nutrition ordinances that implement the national law. Moreover, it argues that ensuring the implementation of stunting prevention program at scale across local governments to produce national impact requires reducing the large inequalities in financial capacity that currently exist. Click here to download the paper.
DP 2019-07: The Evolution of APEC and its Role in Philippine Trade and Investment This paper presents how the Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation (APEC) has evolved as an institution, the changes it has undergone, and the challenges it has faced for the past decades. More importantly, this paper tries to enumerate the roles of APEC in positioning the Philippines in the global economy. Anchored on the desire to promote economic growth, foster and strengthen trade, and improve the living standards in the region, APEC initiated programs focused on trade and investment liberalization, trade facilitation, and economic and technical cooperation. These initiatives help the Philippines stimulate and improve the competitiveness of its domestic producers and sectors. The economy must utilize these initiatives, backed with the upgrading of domestic facilities to meet global standards and the aligning of domestic regulations. These address behind-the-border barriers that limit the flow of goods and services and expand the coverage of businesses to overseas markets. Trade agreements in APEC also help firms gain access to cheaper inputs and more advanced technologies, which foster competition and increased productivity and growth. Click here to download the paper. DP 2019-06: 'Starting Where the Children Are': A Process Evaluation of the This process evaluation determines how the program is proceeding since the passage of Republic Act 10533 or the Enhanced Basic Education Act of 2013. It specifically looked at program theory, service delivery and utilization, and program organization. To capture the breadth of conceptual and implementation issues, 18 randomly selected elementary schools were visited from among private and public school systems, distributed according to Department of Education's (DepEd) typology of small, medium, and large schools; island groupings of Luzon, Visayas, and Mindanao; and from both linguistically diverse contexts and less linguistically diverse communities. Key informant interviews with former and current DepEd officials at the national, regional, and division levels, and focus group discussions with teachers and parents were done. An online survey to determine the extent of implementation at the school level was also conducted. Findings show the breadth of challenges the program is facing emanating from conceptualization to implementation. The online survey revealed that, while almost all schools are implementing the program, the quality of implementation may be wanting as less than 10 percent of schools surveyed have done the four activities required for its implementation. The study recommends improving the implementation of program classified into program logic, service delivery and utilization, and program organization. Overall, the program needs a better appreciation of its existing conceptual problems and the cooperation of all stakeholders for the program to succeed. Click here to download the paper. |
July 25, 2019, 2:00–5:00PM -----------------------------------------
The Philippine Journal of Development is a professional journal published by the Philippine Institute for Development Studies. It accepts papers that examine key issues in development and have strong relevance to policy development. As a multidisciplinary social science journal, it accepts papers in the fields of economics, political science, public administration, sociology, and other related disciplines. It considers papers that have strong policy implications on national or international concerns, particularly development issues in the Asia-Pacific region. CLICK HERE for the guidelines in the preparation of articles. Submissions and inquiries may be sent to PJD@mail.pids.gov.ph. |
|||
The Philippines is slowly aging, according to a study of state think tank Philippine Institute for Development Studies (PIDS). | ||||
POLICY ISSUE AT A GLANCE Forest Protection in the PH: What Have We Accomplished? More than half of the Philippines’ land mass is classified as forestlands, making the country a megadiverse area in terms of tropical forests and biodiverse ecosystems. However, decades of lax legislations promoting extractive industries have led to a significant reduction in forest cover. In 2011, two landmark laws—Executive Orders (EO) 23 and 26—were passed. EO 23 declared a moratorium on logging while EO 26 called for the implementation of the National Greening Program.
"To view in actual size, visit the PIDS website or the PIDS Facebook page.
FACT FRIDAY Every Friday, PIDS releases nuggets of research results culled from different PIDS studies. Here are the latest #PIDSFactFriday issues. Like us on Facebook for more #PIDSFactFriday issues. |
||||
Need help? Have feedback? Feel free to contact us. © 2018 Philippine Institute for Development Studies.
|
||||
 PIDS 2018 Annual Report: Harnessing The Fourth Industrial Revolution: Creating Our Future Today
PIDS 2018 Annual Report: Harnessing The Fourth Industrial Revolution: Creating Our Future Today.jpg)