Having trouble reading this email? View it in your browser. |
||||
 |
||||
|
||||
RESEARCH PAPER SERIES
As several countries have reduced tariff rates, other forms of regulatory measures that impact on trade have proliferated. These regulations, collectively known as nontariff measures (NTMs), can be imposed on imports and exports. Using descriptive indicators, NTMs could be measured with coverage ratios, frequency indices, and prevalence scores. Across the different government agencies, it has been found that the Department of Agriculture and the Department of Environment and Natural Resources both implement the most number of NTMs with 422 and 103 NTMs, respectively. Moreover, both agricultural goods and manufactured goods have been shown to be highly regulated at 92.2 percent and 93.9 percent, respectively, albeit agricultural goods have a higher prevalence score (19.8) compared to manufacture goods (8.9). Click here to download the research paper.
The Philippines is slowly ageing. In a little over a decade, the country's elderly will comprise at least 7 percent of the total population. This rising tide may pose some substantial burden on the country's resources. Nonetheless, the same economic and demographic forces that will eventually lead to population ageing may also provide potentials for economic growth. This paper documents the country's historical experience of the demographic dividend using new National Transfer Account time-series estimates for the Philippines. These estimates also reflect how the interaction between public policy and population ageing may affect household welfare and fiscal balance in the foreseeable future. Click here to download the research paper. RPS 2020-01: Vulnerability to Income Poverty in the Philippines:
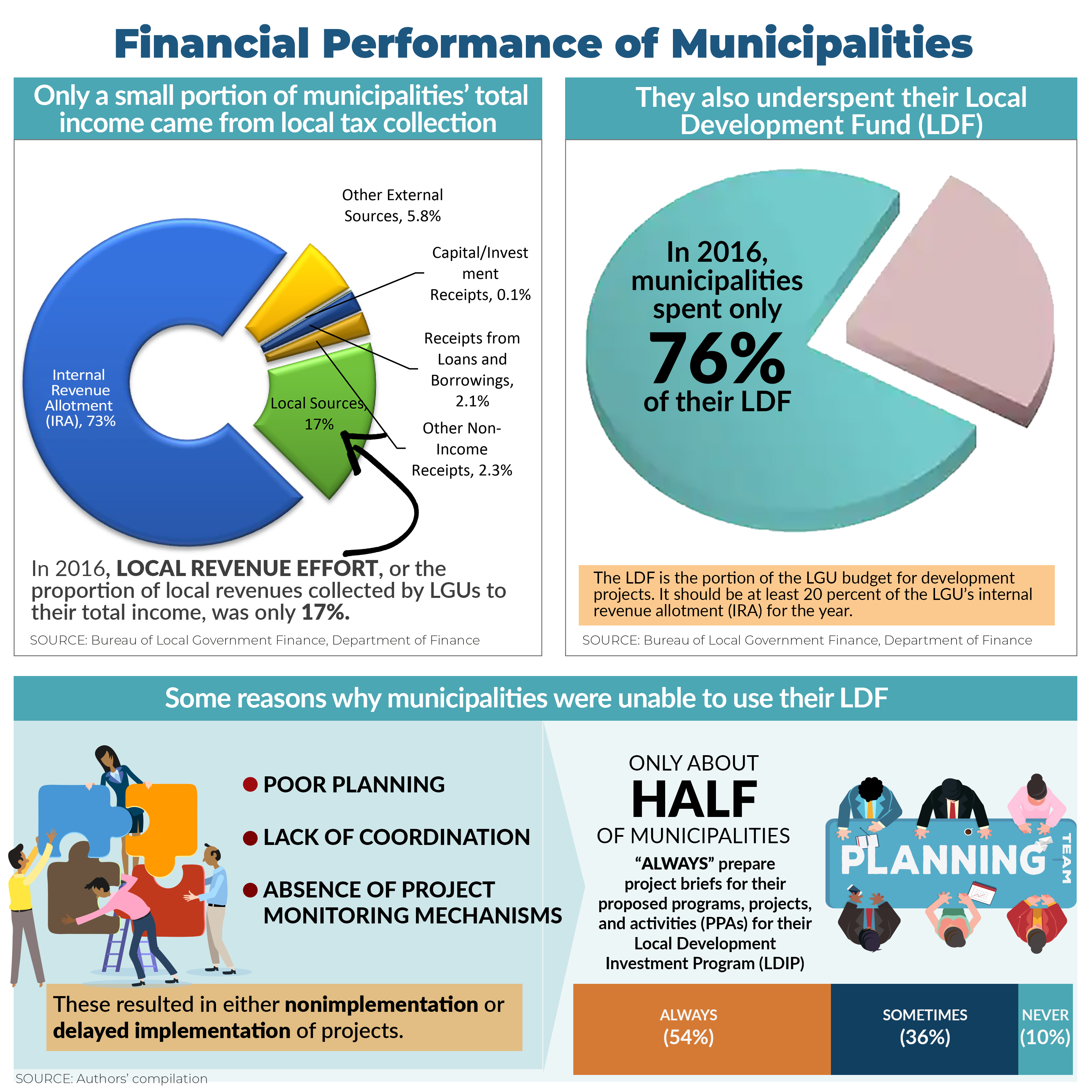
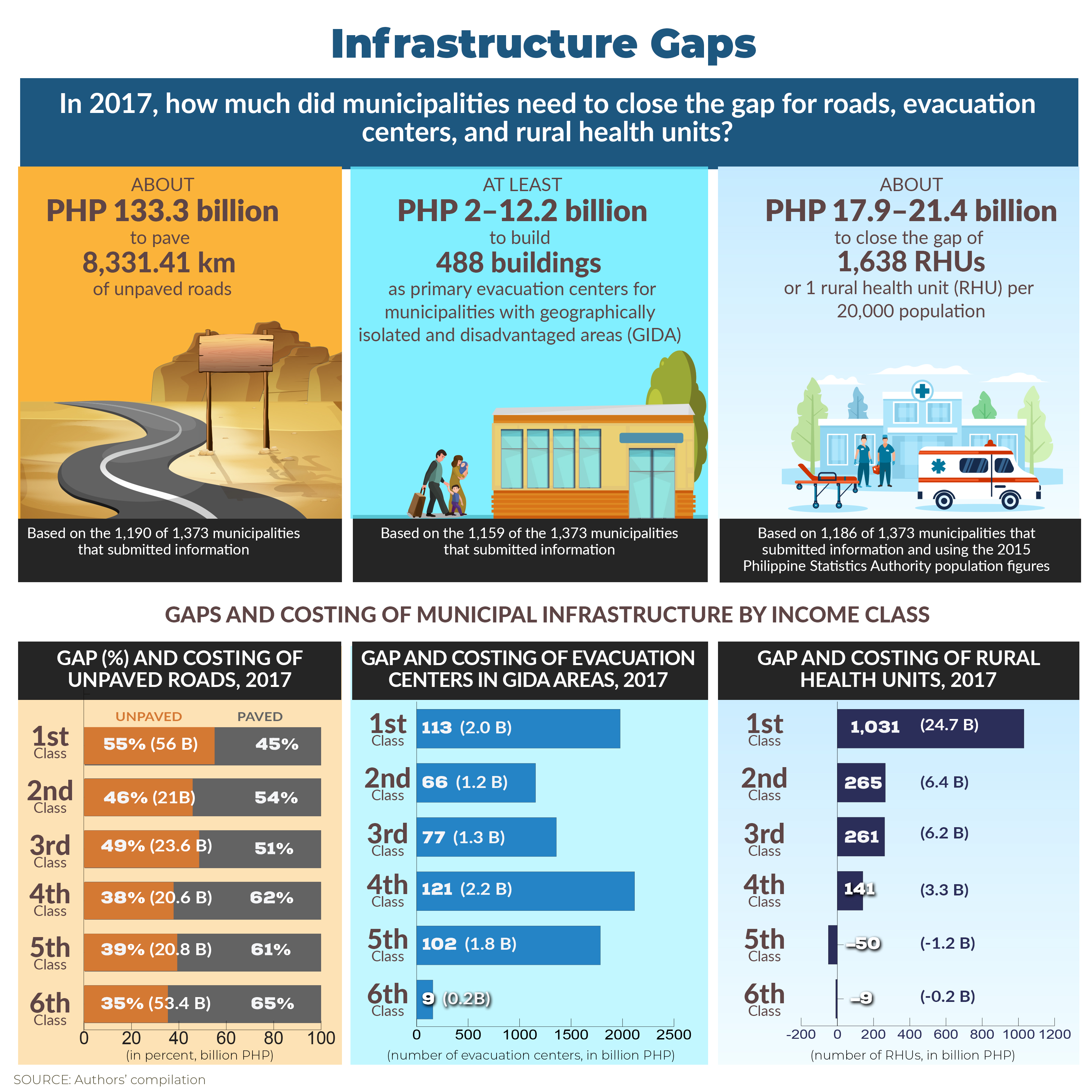
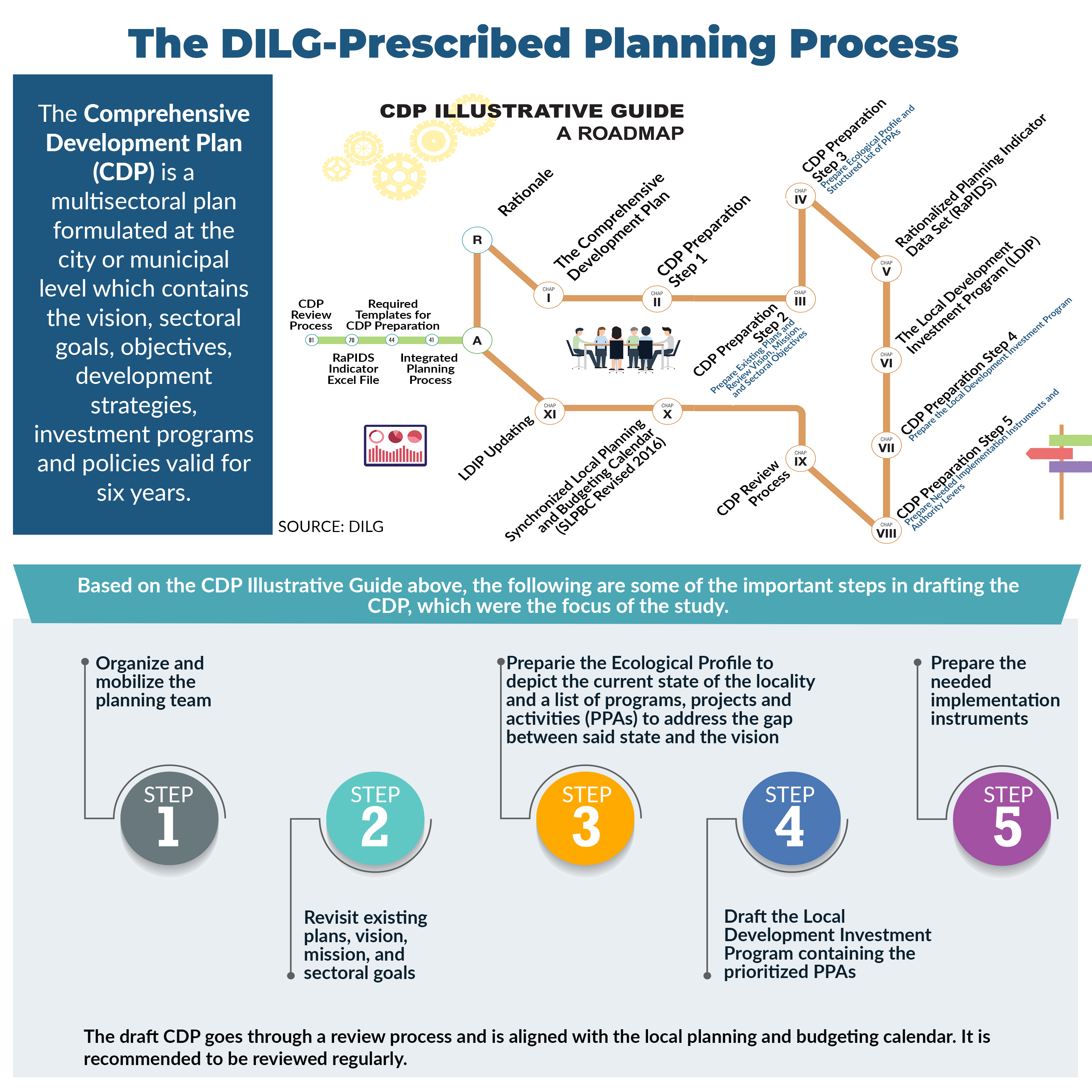
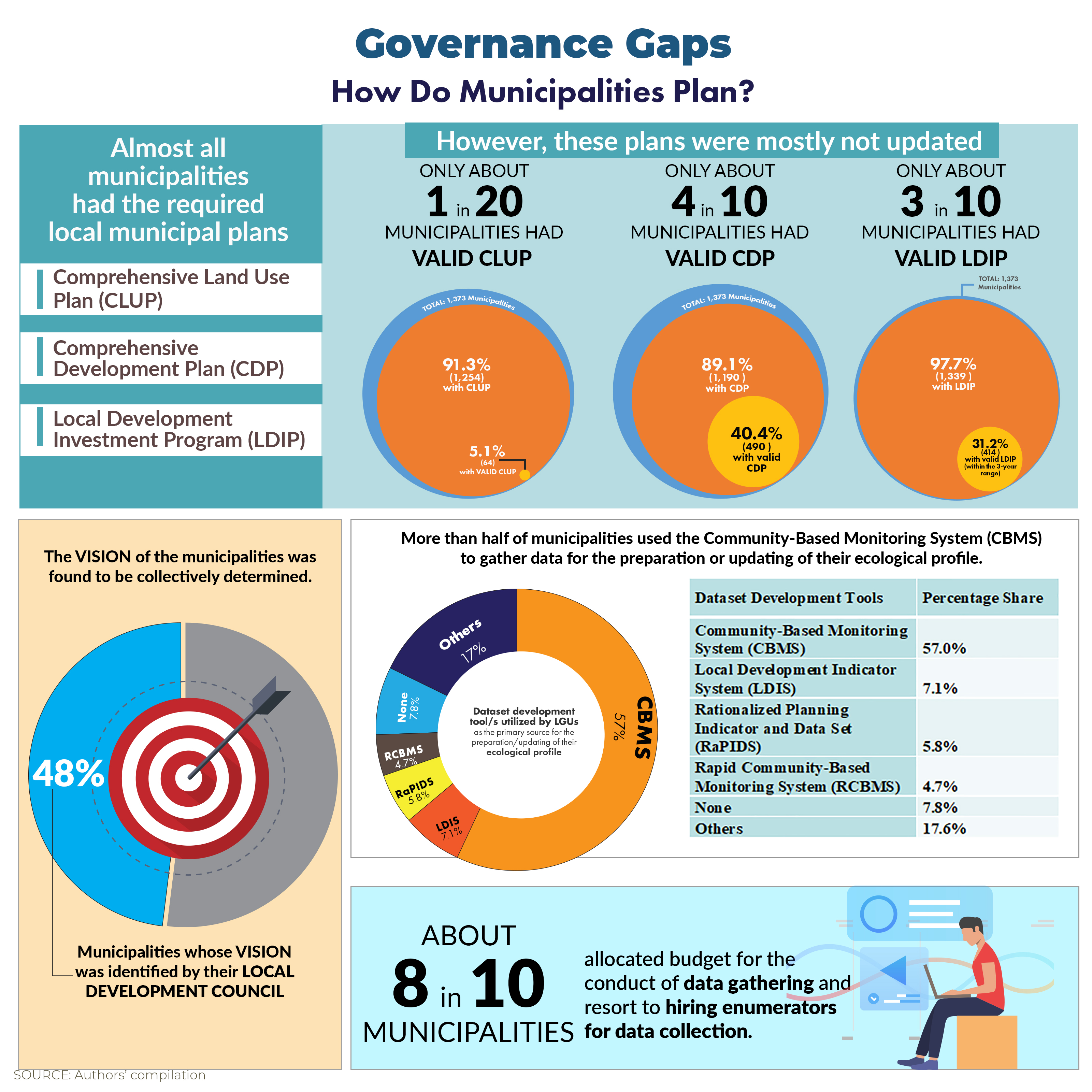
An Examination of Trends This study continues previous work on estimating the vulnerability level of households to income poverty using a modified probit model based on income and other poverty correlates data sourced from the Family Income and Expenditure Survey, as well as the country's official poverty lines. Past model specifications are improved by including data on price and climate shocks to welfare, as well as by generating individual assessments for urban and rural areas before combining the cross-section results, rather than using a common specification nationally as done previously. The vulnerability assessment in this study provides inputs to forward-looking interventions that build the resilience of households for preventing or reducing the likelihood of future poverty. The study emphasizes the importance of using both poverty and vulnerability estimates in programs and identifies differentiated actions for those highly vulnerable and relatively vulnerable to poverty. Click here to download the research paper. POLICY NOTE PN 2020-05: Irrigation Investments: Some Recurrent and Emerging Issues This Policy Note looks at some recurrent and emerging concerns on how to improve irrigation investments in the country. Among others, it finds that despite the increase in allocation, the National Irrigation Administration (NIA) has hardly met its annual physical targets for new area development. Among the reasons behind this are institutional, physical, and operational constraints faced by NIA. In particular, its targeting system appears to be weak as a result of the decline in human resources with needed expertise and experience to perform critical functions. Another cause of concern is the fast conversion of lands, rendering irrigation investments useless. To address these issues, the study calls for a clear understanding of the bottlenecks or limiting factors in achieving the target new areas. It also urges NIA to carefully assess land conversions to redirect investments to areas which are in actual need of irrigation. The study likewise suggests exploring the potential for irrigation investment to support the crop diversification program, given the rice tariffication and the increasing nonviability of rice areas. Click here to download the policy note. DISCUSSION PAPERS DP 2020-06: Efficiency of Local Governments in Health Service Delivery: A Stochastic Frontier Analysis The study analyzes the efficiency implications of fiscal decentralization using stochastic frontier analysis (SFA). It uses health expenditure (in per capita real terms) data from local government units (LGUs) as input. The output variables of interest include access to safe water and sanitation, health facility-based delivery, and access to hospital inpatient services. It also uses LGU income and its major components (i.e., own-source revenue and income revenue allotment, in per capita real terms) as covariates, as well as the health expenditure decentralization ratio to account for fiscal autonomy on the expenditure side. Two measures of fiscal decentralization were also used as factors affecting efficiency to account for financial/fiscal autonomy of the LGUs on the income side, i.e., the ratio of own-source revenue to expenditures and ratio of own-source revenue to income). Issues such as the mismatch between local government fiscal capacity and its devolved functions, health system fragmentation, existence of two-track delivery system, and unclear expenditure assignments, among others, inevitably create inefficiency. These issues should be addressed to fully reap efficiency gains from fiscal decentralization, particularly in health devolution. Click here to download the publication. DP 2020-05: Assessment of the Performance Challenge Fund and the Seal of Good Local Governance: Perceptions from Municipalities Using the results of a nationwide survey of all municipalities in the Philippines, this study focuses on the perceptions of the core members of the municipal planning team on the usefulness and importance of the Perfomance Challenge Fund (PCF). Survey showed that majority of the local government respondents appreciated the PCF and recognized its importance. But evidences also showed that about 20 percent of surveyed municipalities were never eligible to receive the PCF. Most of these municipalities were from the 5th and 6th income class, concentrated in the Bicol, Central Visayas and Eastern Visayas regions. In addition, there were some local government units that were either consistent or inconsistent recipients of the PCF. These results must be considered by policymakers especially with the recent passage of the Seal of Good Local Governance Law. Click here to download the publication. DP 2020-04: Fiscal Decentralization and Health Service Delivery: An Assessment The study proposes an analytical framework that examines the effects of fiscal decentralization on health service delivery using difference-in-differences (DID) method. It draws up the standard measure of the extent/degree of fiscal decentralization affecting the health sector. The findings of the DID analysis suggest that greater health decentralization has a negative impact on access to hospital inpatient services and access to sanitation (toilet). It contradicts the hypothesis of the study that greater health decentralization will result in better health services. Nevertheless, it is consistent with the existing narratives that highlight the lower spending on hospitals at the provincial level due to mismatch between the cost of devolved hospitals and the local government units (LGUs) internal revenue allotment (IRA), i.e., block grant transferred to the LGUs. Such negative effect has remained over the years because most LGUs do not have adequate health budget to maintain and upgrade devolved health facilities. Click here to download the publication. DP 2020-03: Baseline Study on Policy and Governance Gaps for the Local Government Support Fund Assistance to Municipalities (LGSF-AM) Program (Integrated Report) One major challenge faced in assessing the impact of the various national government interventions is the lack of baseline data. This study aims to identify policy and governance gaps in infrastructure and planning to provide baseline data on key areas and current planning practices of local governments. The desk review revealed low revenue effort, as well as inadequate utilization of mandated development fund, due to poor planning in majority of the municipalities. The study recommends (1) improving compliance of LGUs in the regular updating of their multisectoral development plans, (2) revisiting the basis for establishing the current situation of a locality, (3) improving project readiness and feasibility, and (4) strengthening capacity development programs to address governance gaps in development planning. Click here to download the publication. DP 2020-02: Assessing the Resurgent Irrigation Development Program of the Philippines - The study evaluates the effectiveness and efficiency of the government's irrigation program with focus on the technical, physical, and institutional aspects of the performance of communal irrigation systems (CIS). Using primary and secondary data collection, key-informant interviews and focus group discussions with key actors, and walkthroughs to gauge the physical irrigation conditions, the study finds that majority of the sampled CIS are gravity systems, except in some provinces where there are more pump irrigation systems coming from lakes, rivers, creeks, springs, runoff, and ground water. While some rivers tapped have adequate flows for irrigation even during the dry seasons, unreliable water supply is a major problem for majority of the CIS that tap water from less dependable water sources or rely on springs and runoff during long dry months. The study suggests that the presence of a dependable surface water source and a good shallow aquifer, as well as soil type and its suitability to different type of crops, be used as major criteria for irrigation development. On the problem of water supply sources, there should be a concerted and united effort on the part of concerned government agencies and the academe to identify potential sites for diversion dams and storage reservoirs. The Free Irrigation Service Act should also clarify its provisions regarding CIS implementation, among others. Click here to download the publication. DP 2020-01: Assessing the Resurgent Irrigation Development Program of the Philippines - This study evaluates the National Irrigation Systems (NIS) in the Philippines, which consisted of 22 NIS in Luzon and 17 NIS in Visayas and Mindanao and are represented by 151 irrigators associations (IAs). The overall objective is to evaluate the policy, programmatic, and institutional framework governing irrigation development and management for the main purpose of improving irrigation performance and productivity of irrigated lands. The methodological approach to meet the specific objectives consisted of data collection through site visits, field measurements, and key-informant interviews and focus group discussions. Results showed that siltation problems exist in canals of almost all NIS cases, causing reduced flow capacities that deprived the downstream portion from adequate water supply, among others. To improve performance of irrigation systems, good watershed management is needed to prevent the siltation of water courses and, thus, enhance water supply distribution. The National Irrigation Administration should allocate realistic resources for operation and maintenance to improve efficiency in water allocation and distribution from upstream to downstream users. Click here to download the publication.
DEVELOPMENT RESEARCH NEWS DRN 2020-01 Vol. 38 No. 1: New college grads
'mismatched' to their jobs This first issue of the Development Research News (DRN) for 2020 puts light on some key challenges in the Philippine education sector. The banner story talks about the current mismatch between the skills learned by the graduates and those needed by the industry today. This was evident in the data science and analytics field--despite being one of the most in-demand jobs. Articles on the challenges faced by reform programs targeting the country's secondary and higher education are also included in the issue. Another article highlights the high labor migration rates among Filipino workers and the role played by social networks. This issue also features articles on the current situation of Philippine trade and export. It also features stories about the launch of the Institute's first book on gender and the groundbreaking ceremony for the new PIDS building. Completing this issue is an article about poor development planning in the local government--specifically at the city/municipal level--and an infographic on the how the country fares in terms of achieving Sustainable Development Goal 8 (Decent Work and Economic Growth). |
[POSTPONED] March 13, 2020, 8AM–2PM [POSTPONED] March 16, 2020, 8AM–2PM [POSTPONED] March 24, 2020, [POSTPONED] March 26, 2020, 8AM–2PM
The Philippine Journal of Development is a professional journal published by the Philippine Institute for Development Studies. It accepts papers that examine key issues in development and have strong relevance to policy development. As a multidisciplinary social science journal, it accepts papers in the fields of economics, political science, public administration, sociology, and other related disciplines. It considers papers that have strong policy implications on national or international concerns, particularly development issues in the Asia-Pacific region. CLICK HERE for the guidelines in the preparation of articles. Submissions and inquiries may be sent to PJD@mail.pids.gov.ph. |
|||
In view of the Enhanced Community Quarantine, the Philippine Institute for Development Studies (PIDS) will implement the work-from-home scheme until April 14, 2020.
A study published by state think tank Philippine Institute for Development Studies (PIDS) found that women in the Philippines have less access to social protection programs than men, which may result in their vulnerability, instability, and poverty.
A study of state think tank Philippine Institute for Development Studies (PIDS) found that Filipino healthcare professionals are more likely to work in areas where earnings are potentially high and near communities where they were trained.
Data science and analytics (DSA) skills remain underdeveloped in the Philippines despite an increasing demand for DSA professionals with the advent of the Fourth Industrial Revolution (FIRe).
“The Philippine education sector is plagued with a serious systemic problem that requires a systemic solution.”
“Even though women have already attained a lot in terms of education, it does not get translated into their labor market participation.”
The Department of Education’s (DepEd) senior high school (SHS) program made a number of gains but also faced several challenges during the first two years of its implementation.
The Asian Development Bank (ADB) has identified priority areas that the Philippines has to improve on to be able to sustain its economic performance in the medium term.
The implementation of the Mother Tongue-Based Multilingual Education (MTB-MLE) program is being hampered by a number of challenges.
The Philippines has consistently ranked high in international rankings in gender parity. However, realities on the ground show otherwise. Authored by various PIDS researchers, it is the Institute’s first book on gender and development. It consists of six chapters that tackle pressing issues affecting both genders, including persistent gender gaps in education, employment, and wages among the poor and agricultural workers. READ MORE
Despite the growing digital economy in the Philippines, the adoption rate of e-commerce among firms is low, a study published by state think tank Philippine Institute for Development Studies (PIDS) revealed.
Sports and arts tracks are the least offered tracks under the senior high school (SHS) program of the Department of Education (DepEd). |
||||
POLICY ISSUE AT A GLANCE Fiscal and Governance Gaps among Municipalities in the PhilippinesUnder a decentralized setting, local government units are given increased spending and revenue-raising authority, including infrastructure development responsibilities. To identify the fiscal gaps in the devolved infrastructure services such as local roads, evacuation centers, and rural health units as well as the governance gaps in the planning process of municipalities, the Department of the Interior and Local Government (DILG) and the Philippine Institute for Development Studies (PIDS), have embarked on a joint research project called the Local Government Support Fund- Assistance to Municipalities (LGSF-AM) Baseline Study on Policy and Governance Gaps. To view in actual size, visit the PIDS website or the PIDS Facebook page. FACT FRIDAY Every Friday, PIDS releases nuggets of research results culled from different PIDS studies. Here are the latest #PIDSFactFriday issues. Like us on Facebook for more #PIDSFactFriday issues. |
||||
Need help? Have feedback? Feel free to contact us. |
||||